Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
吉田 啓之; Zhang, W.; 三澤 丈治; 大貫 晃; 高瀬 和之
Proceedings of 3rd Asian-Pacific Congress on Computational Mechanics (APCOM '07) & 11th International Conference on Enhancement and Promotion of Computational Method in Engineering and Science (EPMESC-11) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2007/12
Thermal-hydraulic design of the boiling water reactor (BWR) is performed by correlations with empirical results of actual-size tests. Development of a method that enables the thermal-hydraulic design of nuclear rectors without these actual size tests is desired, because these tests take a long time and entail great cost. For this reason we developed an advanced thermal-hydraulic design method for BWRs using innovative two-phase flow simulation technology. In this paper, the numerical results applied to the fluid mixing phenomena in the current boiling water reactor rod bundles and tight lattice rod bundles adopted in the innovative FLexible-fuel-cycle Water Reactor (FLWR) are shown and the existing correlations for the fluid mixing phenomena are evaluated by use of these results. And statistical evaluations of numerical simulation results are also performed to develop analytical method to confirm or modify the correlations for fluid mixing phenomena. In these statistical evaluations, attention was focused on instantaneous fluctuation characteristics of fluid mixing. With the calculation of correlation coefficients between the differential pressure and gas/liquid mixing coefficients, the time scales of fluid mixing were evaluated.
都留 智仁; 渋谷 陽二*; 加治 芳行
Proceedings of 3rd Asian-Pacific Congress on Computational Mechanics (APCOM '07) & 11th International Conference on Enhancement and Promotion of Computational Method in Engineering and Science (EPMESC-11) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/12
金属材料において、結晶粒の微細化によって転位の運動を阻害することがマクロな結晶金属の強化の方法として広く行われてきた。その一方で、粒界部の転位の蓄積によって生じる応力集中は応力腐食割れ(SCC)の大きな要因となるといわれている。しかしながら、その変形メカニズムについての詳細な説明はなされておらず、実験によって転位の運動を直接観察することは困難である。また、変形に対する粒界の影響は結晶粒径だけでなく結晶粒の形状や粒界の種類によって異なるため、転位と粒界の相互作用の基礎的なメカニズムを理解することはますます重要になると考えられる。本研究では、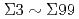 までの対応粒界について粒界エネルギーを原子論的手法を用いて詳細に評価し、状態遷移弾性バンド法によって
までの対応粒界について粒界エネルギーを原子論的手法を用いて詳細に評価し、状態遷移弾性バンド法によって![$$Sigma 3 (111)[110]$$](/search/images/EROFG0LHNVQSAMZAFAYTCMJJLMYTCMC3EQ.gif) 傾角粒界を対象に転位と粒界の相互作用に関するエネルギー的評価を行った。その結果、各対応粒界における粒界エネルギーと粒界による堆積増分に相関関係があり、転位は粒界と相互作用する際にPeierlsポテンシャルに比べて非常に大きな活性化エネルギーを必要とすることがわかった。
傾角粒界を対象に転位と粒界の相互作用に関するエネルギー的評価を行った。その結果、各対応粒界における粒界エネルギーと粒界による堆積増分に相関関係があり、転位は粒界と相互作用する際にPeierlsポテンシャルに比べて非常に大きな活性化エネルギーを必要とすることがわかった。